Book a Dermal Filler Appointment with Dr. Laura Geige at It’s Me and You Clinic
Radiesse is a popular non-surgical cosmetic treatment used to restore lost volume, smooth out wrinkles and fine lines, and enhance facial contours. However, like any medical treatment, it’s essential to carefully evaluate whether you’re an ideal candidate for Radiesse. In this response, we’ll delve into the individuals who should not use Radiesse.
1. **Pregnant or breastfeeding women**: Radiesse is made from calcium hydroxylapatite, a biocompatible material that can potentially cause harm to an unborn fetus or pass into breast milk. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should avoid Radiesse treatments until they’ve completed their pregnancy and ceased breastfeeding.
2. **People with weakened immune systems**: Individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those suffering from HIV/AIDS, cancer, or undergoing chemotherapy, may not be good candidates for Radiesse. Their bodies may have difficulty processing the injected material, which could lead to adverse reactions or allergic responses.
3. **Those with a history of bleeding disorders**: Patients with bleeding disorders like hemophilia or platelet dysfunction should exercise caution when considering Radiesse. The procedure involves injecting a foreign substance into the skin, which can increase the risk of bleeding complications.
4. **People with pacemakers or implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs)**: The presence of these electronic devices increases the risk of complications during Radiesse treatments. A pacemaker’s electrical impulses can interact with the injected material, potentially causing cardiac arrhythmias or other issues.
5. **Individuals with severe allergies**: If you have a history of severe allergic reactions to similar substances, such as lidocaine or antibiotics, it’s best to avoid Radiesse. Your doctor will assess your allergy risk before administering the treatment.
6. **Those with skin infections or inflammation**: Infections like acne, rosacea, or eczema can increase the risk of complications during Radiesse treatments. Patients should allow sufficient time for any active infections to resolve before undergoing the procedure.
7. **People with metal fragments in their body**: The presence of metal fragments, such as those from joint replacements or shrapnel, can interfere with the treatment’s effectiveness and increase the risk of adverse reactions.
8. **Those who have had recent facial trauma or surgery**: Patients who have experienced facial trauma or undergone recent surgeries should allow sufficient time to heal before undergoing Radiesse treatments. This will help minimize the risk of complications and ensure a smooth recovery.
9. **Individuals with certain medical conditions**: Certain conditions, such as bleeding disorders, hematomas, or implantable devices, may increase the risk of complications during or after Radiesse treatments. Patients should discuss their medical history with their doctor before undergoing treatment.
10. **Those who are taking certain medications**: Certain medications, like anticoagulants or antiplatelet agents, can interact with Radiesse and increase the risk of bleeding complications. Patients should inform their doctor about all medications they’re currently taking to ensure safe treatment.
In conclusion, while Radiesse is a safe and effective non-surgical cosmetic treatment, it’s not suitable for everyone. It’s essential to carefully evaluate your medical history and discuss any concerns with your doctor before undergoing Radiesse treatments. By doing so, you can minimize the risk of complications and achieve optimal results from this popular injectable solution.
General Health Conditions
Reserve a Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige Now
Individuals with certain general health conditions may be more susceptible to complications from Radiesse, a non-surgical dermal filler used to treat facial wrinkles and folds. These conditions include:
- Autoimmune disorders: Conditions such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and scleroderma can increase the risk of complications from Radiesse due to their impact on the body’s immune system.
- Pregnancy or breastfeeding: As with any cosmetic treatment, pregnant or breastfeeding women should avoid using Radiesse until after they have completed these life stages.
- Severe skin conditions: Certain skin conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, and rosacea may increase the risk of complications from Radiesse due to their impact on skin health.
- Allergies: Individuals with allergies to lidocaine or other medications used in Radiesse should consult a doctor before undergoing treatment.
Additionally, individuals with certain medical conditions may be more at risk for complications from Radiesse:
- Herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection: Patients with active HSV infections should avoid using Radiesse until the infection has been fully cleared up.
- Actinic keratosis or sun damage: Individuals with skin damage due to excessive sun exposure may be more prone to complications from Radiesse.
- Wound healing problems: Patients with difficulty wound healing, such as those with diabetes or poor circulation, should exercise caution when undergoing Radiesse treatment.
Other medical conditions that may increase the risk of complications from Radiesse include:
- Fibromyalgia: This chronic condition can affect pain perception and lead to increased sensitivity to Radiesse injections.
- Multiple sclerosis: Patients with this condition should consult a doctor before undergoing Radiesse treatment, as it may exacerbate symptoms.
It is essential for individuals considering Radiesse treatment to discuss their medical history with a qualified healthcare professional or dermatologist to determine if they are suitable candidates for the procedure.
- Patient’s with active infections may not be ideal candidates for Radiesse treatment due to the increased risk of infection and the potential for the filler material to spread to other parts of the body.
- People with bleeding disorders like hemophilia or thrombocytopenia should use Radiesse with caution, as the filler material can increase the risk of bruising and bleeding.
- Patients undergoing immunosuppressive therapy may need to consider alternative options for facial fillers due to the weakened immune system, which can make it more difficult for the body to reject foreign materials.
- Individuals with severe respiratory diseases such as asthma or COPD should exercise caution when considering Radiesse treatment, as the filler material can potentially cause respiratory problems if not handled properly.
These individuals may need to consider alternative options for facial fillers or discuss their medical conditions with a qualified healthcare professional before undergoing Radiesse treatment. A thorough evaluation and consultation can help determine the best course of treatment for each individual.
It’s also worth noting that some patients may be at higher risk of complications from Radiesse due to underlying medical conditions, such as:
- Autoimmune disorders like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis, which can increase the risk of an allergic reaction to the filler material.
- Neurological disorders, such as multiple sclerosis or Parkinson’s disease, which can affect sensation and movement in the face.
- Cardiovascular conditions, such as heart failure or hypertension, which can increase the risk of complications from facial fillers.
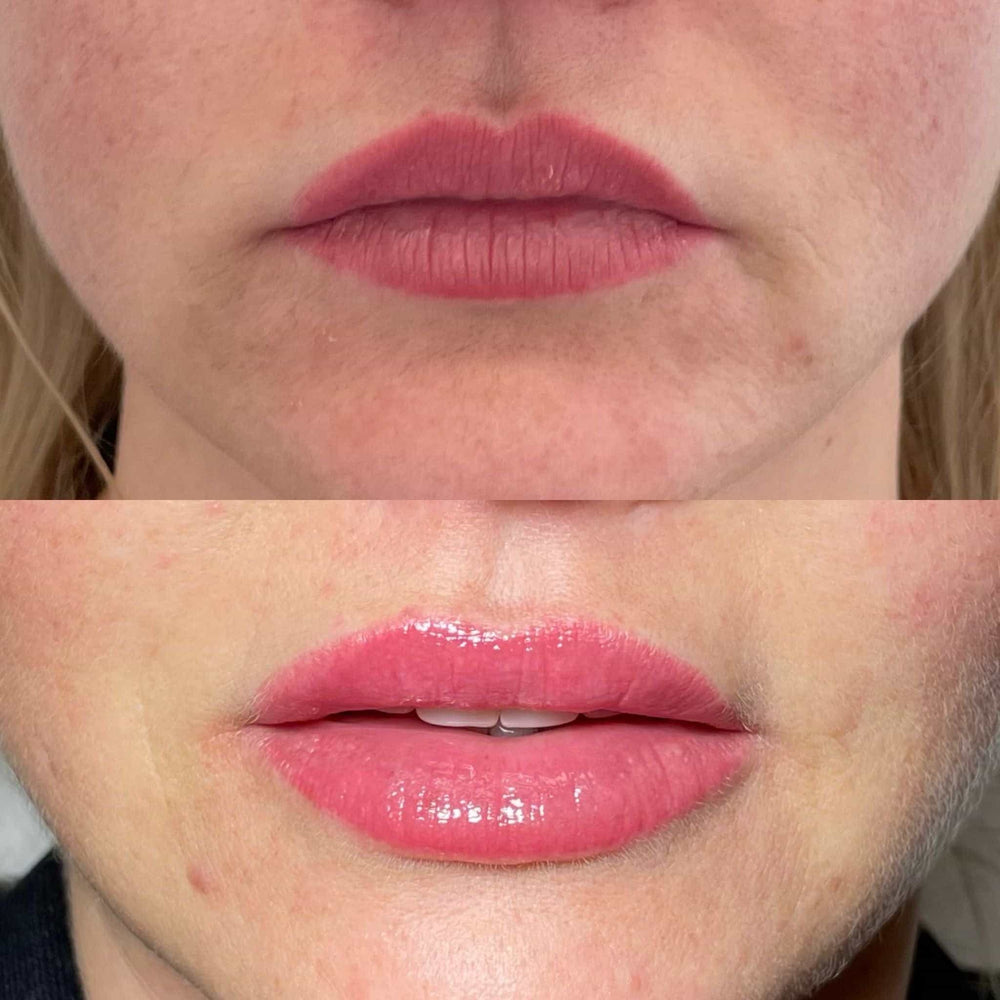
In these cases, it’s essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional before undergoing Radiesse treatment. They can assess individual risks and provide guidance on the best course of treatment.
Medications and Supplements
The safety and effectiveness of Radiesse, a non-surgical injectable dermal filler, depend on various factors, including an individual’s medical history and current medications. Certain medications and supplements may interact with Radiesse or increase the risk of complications.
Blood Thinners: Patients taking blood thinners, such as warfarin (Coumadin), aspirin, or heparin, should not use Radiesse. These medications can prolong bleeding time and increase the risk of bruising and hematoma formation at the injection site.
Steroids: The use of steroids, such as prednisone, can lead to an increased risk of infection and impaired wound healing. Patients taking steroids may be more susceptible to complications after Radiesse treatment.
Certain Supplements: Some supplements may interact with Radiesse or increase the risk of complications. These include:
- St. John’s Wort:** This herb can affect the metabolism of Radiesse, leading to increased levels in the body.
- Fish Oil/Omega-3:** While generally considered safe, high doses of fish oil/oxygen-3 may increase the risk of bruising and bleeding at the injection site.
- Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Medications such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) or naproxen (Aleve) can increase the risk of bleeding and bruising.
Anticoagulant Medications: Patients taking medications like Plavix (clopidogrel) or Xarelto (rivaroxaban) should avoid using Radiesse, as these medications can increase the risk of bleeding.
Beta Blockers: Beta blockers, such as Propranolol (Inderal), may affect the heart rate and blood pressure responses to Radiesse.
Vitamin Supplements: High doses of vitamin K can increase the risk of bleeding. Patients taking high doses of vitamin K supplements should use Radiesse with caution.
Ginkgo Biloba: This supplement may increase the risk of bleeding and bruising at the injection site when used in combination with Radiesse.
Caffeine: High levels of caffeine can increase heart rate and blood pressure, which may interact with the effects of Radiesse.
It is essential to inform your healthcare professional about all medications, supplements, and medical conditions before undergoing Radiesse treatment. Your doctor will assess the risks and benefits and provide personalized guidance on safe treatment options.
Medications and supplements can significantly impact the outcome of treatments involving Radiesse, a dermal filler made from calcium hydroxylapatite. It’s essential to understand which medications and supplements may increase the risk of complications or interact with the treatment.
One group of medications that may pose a risk is steroids. Long-term use of steroids can lead to atrophy of the skin, causing it to become thinner and less responsive to Radiesse injections. This can result in a less effective outcome and may require additional treatments to achieve the desired results.
Another category of medications that should be used with caution when combined with Radiesse are blood thinners such as warfarin or aspirin. These medications increase the risk of bleeding, and when combined with Radiesse, this risk can become even more significant. Patients taking these medications may require additional precautions to minimize the risk of complications.
Immunosuppressive drugs like cyclosporine or tacrolimus are another group that should be used with caution when undergoing treatment with Radiesse. These medications suppress the immune system, and their interaction with Radesse can lead to unpredictable reactions and increased risk of complications.
It’s also crucial for patients taking certain supplements to inform their doctor before undergoing Radiesse treatment. Supplements containing calcium, vitamin K, or other nutrients that may interact with the treatment should be disclosed. For example, high levels of vitamin K can increase the risk of bleeding when combined with Radesse.
Other supplements that may interact with Radesse include omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin E, and ginkgo biloba. These supplements can affect blood clotting and increase the risk of bleeding when used in conjunction with Radesse.
Avoiding these medications and supplements before undergoing Radiesse treatment is crucial to minimizing the risk of complications and achieving optimal results. Patients should consult their doctor before treatment to discuss any medications or supplements they are taking and determine the best course of action.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Radiesse, a dermal filler made from radioactive calcium hydroxylapatite, has been used to treat various facial wrinkles and folds. However, its potential risks and complications have raised concerns about its safety during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
When it comes to the unborn child, exposure to Radiesse could pose significant risks due to the radioactivity present in the filler.
The radioactive material in Radiesse, known as calcium hydroxylapatite, emits ionizing radiation, which can pass through the skin and into the bloodstream. This radiation has the potential to reach the fetus through the placenta during pregnancy.
Studies have shown that exposure to low levels of ionizing radiation during embryonic development can lead to genetic mutations and increased risk of cancer later in life. While the amount of radiation released from Radiesse is considered negligible by regulatory agencies, some experts caution that it’s still not without risks.
Pregnant women who undergo treatments with Radiesse are at a higher risk of exposure to ionizing radiation, which could affect their unborn child. This increased risk is particularly concerning in the first trimester, when the fetus is most vulnerable to genetic mutations and developmental disruptions.
Furthermore, breastfeeding mothers may also be exposing their infants to small amounts of radioactive material through milk production. Although the levels are likely to be extremely low, some experts argue that this still constitutes a potential risk.
Given these concerns, women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should exercise caution when considering treatments with Radiesse. If they must undergo treatment, it’s recommended that they discuss alternative options with their healthcare provider and carefully weigh the potential risks against any benefits.
Additionally, regulatory agencies such as the FDA have issued guidelines advising against using Radiesse in pregnant women. Healthcare providers should be aware of these guidelines and consult with their professional organizations for guidance on managing patients who are pregnant or breastfeeding.
In summary, while the exact risks associated with Radiesse exposure during pregnancy and breastfeeding remain unclear, the potential consequences highlight the need for caution and careful consideration when using this dermal filler in vulnerable populations. Women who must undergo treatment should be informed of the possible risks and explore alternative options whenever possible.
Radiesse treatment is a popular cosmetic procedure that involves injecting hyaluronic acid and calcium hydroxylapatite into the skin to stimulate collagen production, reduce fine lines and wrinkles, and improve skin texture. However, as with any medical treatment, there are certain individuals who should avoid undergoing Radiesse or approach it with caution during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
The main concern is the lack of research on the effects of Radiesse on unborn children. As a precautionary measure, women who are pregnant or breastfeeding are advised to discuss alternative options with their healthcare provider before proceeding with any cosmetic procedure.
This recommendation is based on the fact that hyaluronic acid, one of the key ingredients in Radiesse, can potentially cross the placenta and affect fetal development. While the risk is considered low, it is still a concern for many women who are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Additionally, some studies have raised concerns about the potential effects of Radiesse on breast tissue, particularly during breastfeeding. The FDA has not conducted extensive research on this topic, and more studies are needed to fully understand the risks associated with using Radiesse during lactation.
In light of these concerns, it is essential for women who are pregnant or breastfeeding to take a cautious approach when considering Radiesse treatment. This may involve delaying the procedure until after pregnancy and breastfeeding have ended.
In the meantime, there are alternative cosmetic treatments that can provide similar benefits without posing a risk to the developing fetus or milk supply. These alternatives may include injectable fillers made from non-animal-derived materials, chemical peels, microdermabrasion, or laser skin resurfacing.
The FDA recommends that women who are pregnant or breastfeeding discuss these alternative options with their healthcare provider before making a decision about Radiesse treatment. A qualified healthcare professional can help weigh the potential benefits and risks of each option and provide personalized guidance on the best course of action.
In summary, while Radiesse treatment may be safe for many women after pregnancy and breastfeeding have ended, it is essential to exercise caution during these critical life stages. By discussing alternative options with a healthcare provider, women can make an informed decision about their cosmetic care that prioritizes their health and well-being.
Radiesse is a non-surgical cosmetic treatment that uses dermal fillers to restore lost volume and smooth out wrinkles and folds. However, like any medical procedure, it’s essential to consider certain individuals who may be contraindicated or should avoid using Radiesse.
One of the primary groups that should exercise caution when considering Radiesse is pregnant women. According to the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS), there is limited data on the use of dermal fillers during pregnancy, and the safety and efficacy of these treatments in this population are not well established.
As a precautionary measure, many plastic surgeons recommend avoiding dermal filler injections during pregnancy due to the potential risks associated with immunomodulation, blood clotting, and other systemic effects. Additionally, some studies have raised concerns about the use of certain fillers, such as hyaluronic acid-based products, in pregnant women due to their potential ability to cause uterine contractions.
Another group that should be cautious when using Radiesse is breastfeeding mothers. While there is no definitive evidence against the use of dermal fillers during breastfeeding, some studies suggest that immunomodulation and other systemic effects may pass into breast milk, potentially posing a risk to the infant.
The ASPS recommends that breastfeeding women consult with their healthcare provider or a qualified plastic surgeon before undergoing any cosmetic procedure, including Radiesse. It’s essential for these individuals to weigh the potential benefits against the risks and consider alternative treatment options that may be safer during this critical period of lactation.
Furthermore, certain medical conditions can also contraindicate the use of Radiesse. For example, patients with autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus, should exercise caution when using dermal fillers due to the potential for immune system modulation and increased inflammation.
Additionally, individuals taking immunosuppressive medications or undergoing chemotherapy may also be at risk for adverse reactions to Radiesse. The NIH recommends that patients discuss their medical history, including any medications or treatments they are currently receiving, with their healthcare provider before undergoing any cosmetic procedure.
Other factors that may affect an individual’s suitability for Radiesse include previous allergies or sensitivities to the ingredients used in the filler product, as well as a history of bleeding disorders or blood clotting issues. Patients with these conditions should consult with their healthcare provider or a qualified plastic surgeon before undergoing treatment.
Book a Consultation for Dermal Fillers at It’s Me and You Clinic with Dr. Laura Geige
Finally, it’s essential to note that while Radiesse is generally considered safe for most adults, certain individuals may experience more significant risks than others due to age-related factors, such as increased blood clotting tendencies or decreased collagen production. Patients over 50 years old should consult with their healthcare provider or a qualified plastic surgeon before undergoing treatment.
Read more about K Aesthetics Studio here. Read more about Fringe Beverly Hills here. Read more about Otherwheres Magazine here. Read more about Arielle Likes to Cook here.
- Neck Line Filler Treatment Near Carshalton, Surrey - May 9, 2025
- Do Cheek Fillers Make Your Face Look Younger? - May 9, 2025
- Cosmelan Depigmentation Peel How To Reduce Pigmentation Effectively In The UK - May 7, 2025